It will be the largest wind farm in the southern hemisphere and is estimated to require an investment of $1bn.The project is being developed by a 50/50 joint venture of AGL Energy and New Zealand-based power generating company Meridian Energy.
In addition to sharing the cost of the wind farm, which is estimated to be $984m, AGL will invest further $27m in the substation which will be completely owned by the company.The wind farm will be capable of powering an average of 220,000 households in Victoria while eliminating 1.7 million tons a year of green house gases.
The output of the plant will be purchased and all the renewable energy certificates will be acquired by AGL.The project will help to partially meet the government’s expanded renewable energy target to produce 9,500MW of renewable energy by 2020.
Macarthur wind farm details
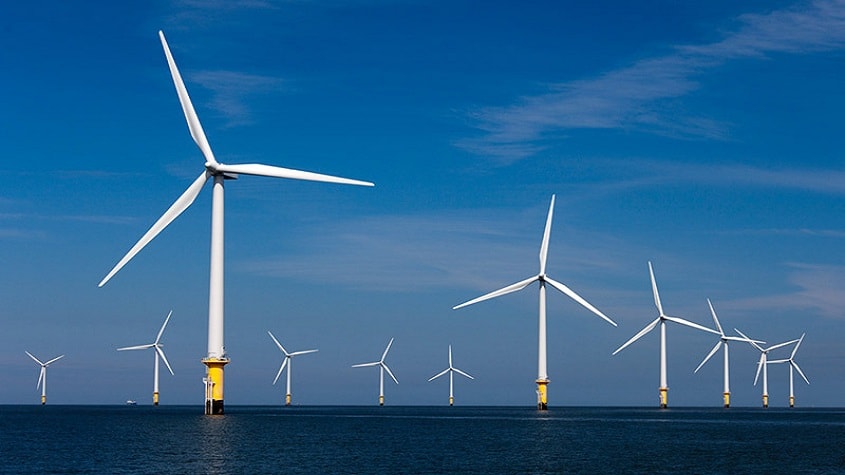
“Macarthur is a 420MW wind farm being constructed near Hamilton, 260km west of Melbourne.”The wind farm is being constructed over 5,500ha of agricultural land between the townships of Macarthur, Hawkesdale and Penshurst in the western districts of Victoria.
The site was chosen due to potential wind harvesting capacity, existing transmission lines and community support.Macarthur wind farm will feature 140 Vestas V112-3.0MW wind turbines.The original plan was to use 2.4MW turbines, which would have required 174 towers.
The decision to use higher capacity wind turbines has reduced the number of towers from 174 to 140. It will also help to achieve substantial savings of $30m in the operational cost over the life of the wind farm.
The turbines will be connected via 90km long underground cables which will be connected to a sub-substation at the site and also to the terminal substation at Tarrone.
Development of the Australian wind farm
The project was proposed in 2004 and approved by the Victorian Government in October 2006. Site clearance and civil works commenced in the fourth quarter of 2010 with the first turbine expected to be on-site by the third quarter of 2011.
The ecological impact on the surrounding flora and fauna was assessed by Australia’s Brett Lane & Associates (BL&A).
Allens Arthur Robinson provided financial advisory services to Meridian Energy in order to form a joint venture with AGL Energy to develop the Macarthur wind farm.
US-based engineering and construction company KBR was awarded the project management services contract in February 2011.
The engineering, procurement and construction (EPC) contract has been awarded to a consortium of Leighton Contractors and Vestas. The contract also includes ten year service agreement and the supply of Vestas SCADA solution.
NOSKE Group will transport the turbine towers, blades, hubs and containers from Keppel Prince Engineering, the point of manufacture, to the project site for Leighton Contractors.
Technology incorporated by the Macarthur wind farm
The Vestas V112 turbine has a maximum blade tip height of 140m, rotor diameter of 112m and 9,850m² of sweep area.
“The wind farm will be capable of powering an average of 220,000 households in Victoria.”
The turbine system comes with options such as condition monitoring systems, smoke and ice detectors, and a fire extinguishing system. It is ideally suited for use where sound-level limits are in force. The blades are designed to be less sensitive to dirt, which results in better performance at sites affected by salt, insects and other air articles.
The state-of-the art CoolerTop technology cools the water used in the turbine cooling system by channelling wind into the heat exchanger. This results in lower energy consumption for cooling the turbine.
Wind farm construction
The project will require 56,000m³ of concrete pour for 8,400t of concrete reinforcement. It also includes laying of 90km of on site access tracks, installation of 420 turbine towers and blades, 140 hubs and 280 containers.
Grid network
Power generated at the Macarthur wind farm will be transmitted to Tarrone substation via 12km long 132kV overhead transmission line.