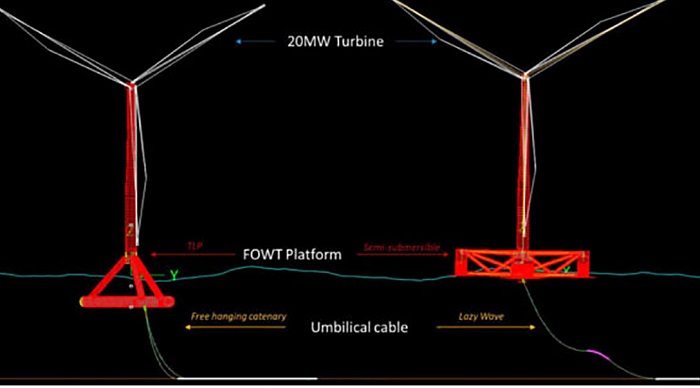
The report assesses through-life performance of Tension Leg Platforms (TLP) compared to Semi-Submersible alternatives for Floating Offshore Wind Turbines (FOWT). In-depth analysis covers several key areas including platform sizing, assembly and fabrication arrangements, quayside and port operations, tow and stability, mooring and cable installations, mooring hook up and operation performance.
Moreover, the report meticulously examined the benefits and drawbacks associated with both SemiSub’s and MPS’ PelaFlex TLP system across various stages of operation.
The report highlights PelaFlex’s significant advantages, in terms of its smaller footprint and enhanced stability post-installation – crucial for maximising turbine output, optimizing overall operational efficiency and ensuring long-term reliability of critical components. Noting options to further streamline the installation process, the report concludes that PelaFlex has potential to emerge as a highly viable solution, offering enhanced performance and efficiency across a wide range of project scenarios.
Work was led by Tadek Senior Engineer Nigel Terry alongside Senior Naval Architects Diogo Nunes and Dr Daniela Benites. It represents a highly interesting piece of analysis for the floating wind sector at large, according to Mr Terry.
“We frequently see comparisons between different floating offshore wind systems, but few studies look at the key aspects we are covering which are critical to a commercially viable FOWT project.” he said. “Utilising a tool developed in-house, we were able to size a Semi-Submersible floater to perform a broad series of comparative studies with MPS’s PelaFlex platform. We discovered the PelaFlex system had a greater number of advantages, including the floater size, assembly and quayside operation, due to its smaller footprint and draft, fewer components and lighter weight. In terms of overall performance, limited motions displayed by PelaFlex, resulted in greater power efficiency and greater workability potential, essential for O&M activities – which we think is vital in the overall cost effectiveness and viability of FOWT.”
“One particular outcome of this benchmarking is the umbilical cable design, where the suppressed motions of the TLP directly benefit the integrity and reliability of umbilical cables,” added Dr. Daniela Benites. “As an example, the cable’s fatigue life is improved, and a less complex configuration is required, reducing the associated installation and operational costs of the FOWT system.”
Established in 2010, Tadek delivers specialist consultancy, complex analysis, engineering solutions and practical project delivery for marine, offshore and subsea projects. Tadek Founder and CEO Rupert Raymond said the recent project for Marine Power Systems highlights the firm’s ‘obsession’ for seeking the ‘engineering truth’ and delivering excellence for clients.
“Tadek benefits from a highly qualified and academically gifted team,” said Mr Raymond. “However, it’s our operational experience in the field which differentiates us from other consultancies on the market. When opportunities arise, we send engineers out on assignments to gain first-hand experience. In this respect, we offer a combination of front-line engineering expertise with complex desk-based analysis. This approach ensures we’re able to ask the right questions, to really challenge and explore solutions, before making detailed recommendations informed by academic principles and real-life application.”
Marine Power Systems’ TLP technology, PelaFlex, was awarded a Statement of Feasibility by independent certification body, DNV, in September 2023, following a comprehensive certification process. The modular floating platform supports the rapid deployment of industrial scale floating offshore wind whilst maximising local content delivery through the existing supply chain.
High system stability, low overall mass and zero tilt maximises energy yields. In addition they allow for simple installation using standard vessels and increases operation and maintenance weather windows. Multiple launch options and the shallow draft support a distributed port model for faster deployment and reduces the need for specific port requirements.